How to Increase Sodium Levels in Elderly Naturally
As we age, many aspects, vital to our health are overlooked, including the balance of electrolytes in our bodies, particularly sodium. Sodium is a significant electrolyte that helps maintain nerve function, blood pressure, and overall well-being.
Unfortunately, the imbalance in sodium levels is often seen as we age. This can cause certain serious consequences and should be addressed timely for better and more effective intervention. This article will help you explore some strategies to increase sodium levels naturally, signs of low sodium levels, and how low sodium levels can have serious consequences for elderly people.
How to Naturally Increase Sodium Levels?
There are several ways to increase sodium levels in the elderly through natural means. One of the most easiest and effective ways is through the dietary modification of the elderly.
Dietary Modification
Make modifications to the eating and consuming habits of the elderly to ensure an increase in their sodium levels.
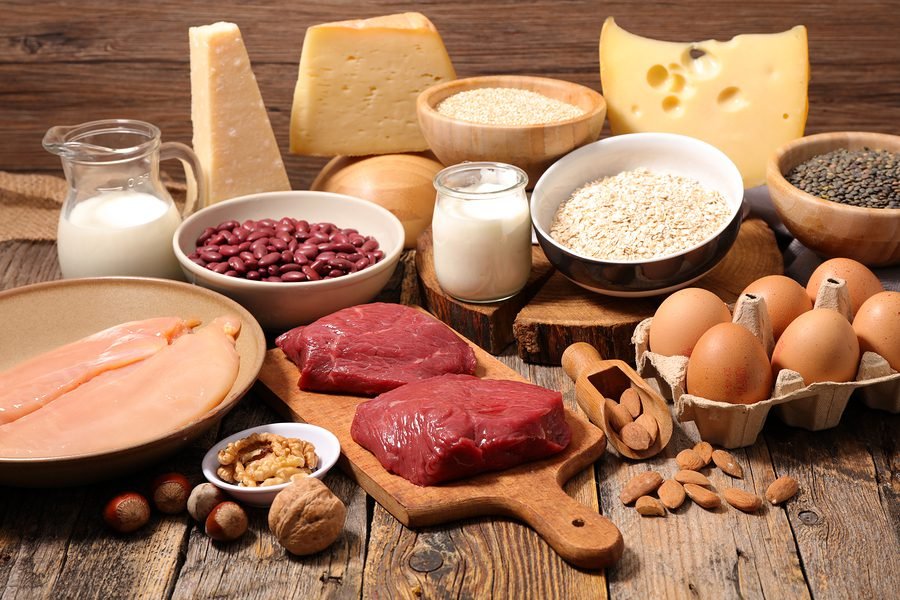
Consume Sodium-Rich Foods
Sodium-rich foods are easily accessible and can be consumed to increase sodium levels naturally in the elderly. Eat vegetables like spinach, kale, celery, and beet in meals. Use dairy products including milk, yogurt, and cheese in daily life. Start consuming food with protein such as fish, eggs, and poultry. Moreover, whole grains like bread, oats, and rice naturally have sodium and can also be consumed to increase sodium levels.


Add Healthy Salts to Meals
Natural salt or Himalayan salt can be used in foods. Moreover, sprinkling a pinch of salt on your salad, cooked vegetables, or meat can help increase sodium content.
Consume Electroluty-Rich Beverages
Coconut is found to be a natural source of sodium, potassium, and magnesium. Coconut water can be used as a beverage to naturally increase sodium levels in the body. Moreover, homemade electrolyte drinks can be prepared using citrus fruits, water, and a pinch of salt, helping in an increase of sodium content in the body.
Hydration
Keeping oneself hydrated can also significantly help in keeping sodium levels maintained in our body.
Importance of Proper Hydration
Maintain the hydration levels through adequate water intake. 15.5 cups for men, while 11.5 cups for women are considered a healthy daily fluid intake option.
Electrolyte-Enhanced Water Option
Consider certain electrolyte-enhanced water options to maintain the sodium levels in our body. Certain sports drinks can be consumed for electrolyte balance during demanding or tough activities such as running, exercise, or swimming.
Lifestyle Modifications
Other than dietary and hydration options, lifestyle modifications can also contribute to a balanced level of sodium content in our bodies and a healthy way of life in the elderly.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in daily exercise can significantly help promote fluid balance. Exercises such as swimming, running, or yoga are good for the optimal functioning of our bodies and should be included in the daily routines of the elderly to help them stay active and healthy.


Managing Stress Levels
Stress is also known to be a contributing factor to sodium imbalance. Practice stress-managing exercises such as meditation or deep breathing to reduce stress levels. Having low stress levels can have a significant effect on emotional health contributing to the overall well-being of an individual, particularly the elderly.
Also, Read: Failure To Thrive In Elderly – All You Need To Know
What role does Sodium Level play in Electrolyte Balance?
Electrolytes are minerals in the body that carry an electric charge when dissolved in bodily fluids or blood. They are essential for various functions such as nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and fluid balance.
Specifically, sodium is the primary extracellular cation in the body, meaning it is found outside of cells in the fluid surrounding them. Alongside other electrolytes like potassium, chloride, and magnesium, sodium helps regulate fluid balance by influencing the movement of water across cell membranes. This movement is critical for maintaining proper hydration levels within cells and throughout the body.
Sodium also plays a significant role in nerve impulse transmission and muscle function. It helps generate action potentials, which are electrical signals that allow nerves to communicate with each other and muscles to contract. Without adequate sodium levels, nerve signaling and muscle function can be impaired, leading to symptoms such as weakness, cramping, and confusion.
Signs of Sodium Imbalance in Elderly
Families and caregivers can pay attention to certain signs below that may hint at low or high sodium content in the bodies of their loved ones.
Fatigue
Both hyponatremia (low sodium content ) and hypernatremia (high sodium content) can lead to fatigue in the elderly. This weakness can interfere with their ability to carry out everyday tasks effectively and impact their independence.
Cognitive Changes
Individuals with hyponatremia may have to deal with confusion, disorientation, or memory problems. However, in the case of hypernatremia, individuals encounter restlessness or irritability.
Nausea
Low sodium levels can also cause nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. This can lead to feelings of weakness or fatigue, hindering the daily life functioning of the elderly.
Headache
Hyponatremia can also cause headaches and muscle weakness in the elderly. This may lead to irritability and severe behavioral changes in elder people.


Changes in Urination
In both hyponatremia and hypernatremia, elderly individuals encounter a change in their urination pattern. A change in the color of urine is observed, while a change in urine output is also a cause of imbalanced sodium levels.
Increased Thirst
In hypernatremia, dehydration is common, leading to a dry mouth and decreased urine output.
Seizures
In critical cases of sodium imbalance, particularly hypernatremia, elderly people may encounter seizures or even coma.
Swelling or Edema
In some cases of hyponatremia, fluids accumulate in tissues leading to swollen hands, feet, or ankles.
Must Read: TOP 7 Pros And Cons Of Long-Term Care Facilities
What are the Challenges in Maintaining Sodium Levels?
Sodium levels can be hard to manage in the elderly population as certain factors are to be considered before providing a solution to their problems.
Dietary Preferences
Individuals may have certain dietary preferences that can contribute to either low levels of sodium or high levels. Their dietary preferences can either limit their intake or exceed the normal amount of sodium intake, leading to complications and issues later in life.
Health Conditions
Certain health conditions such as kidney disease, heart disease, or liver disease can contribute to an alteration in sodium levels. Moreover, the use of certain prescribed medications, related to certain diseases can hurt sodium content, including fluid imbalance, leading to severe complications, particularly in the elderly.
Individual Differences
The sodium requirement of each individual may vary on several factors such as age, gender, or overall health. Evaluating the health conditions and determining the levels of sodium required for overall health is crucial but can be hard for healthcare professionals to assess.
Hydration and Fluid Balance
Fluid balance and hydration are closely related. Any slight change in hydration due to diarrhea or vomiting can lead to serious complications related to sodium imbalance. It is more complex in the case of the elderly as they may impaired thirst or difficulty accessing fluids and keeping themselves hydrated.


What is the Impact of Low Sodium Levels on Elderly People?
Hyponatremia (low sodium level) can have serious adverse effects on the health and overall well-being of elderly individuals.
Cognitive Impairment
With confusion and disorientation, individuals with low sodium intake may also encounter memory problems and difficulty with cognitive patterns. However, in the case of elderly people, these symptoms may be confused with dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, which are also quite common in old age.
Increased Risk of Falls
With fatigue, nausea, and muscle weakness, individuals with low sodium levels are at risk of falls. This can have serious consequences including major injuries or fractures.
Muscle Weakness
Low sodium levels can impact nerve signaling and muscle function, leading to muscle weakness and cramps. Elderly individuals may already be experiencing age-related muscle weakness, making them more susceptible.
Severe Complications
Individuals with abnormal sodium intake are at more risk of complications, including seizures, edema, or coma. Moreover, the elderly may be more vulnerable to such complications as their immune system weakens over time and due to age-related physiological changes.
Impact on Quality of Life
With hyponatremia, the quality of life of individuals is greatly impacted. They may begin to encounter confusion and sudden changes in behavior. It can also lead to hospitalization, medical interventions, and an increase in healthcare costs.
Editor’s Pick: Sudden Excessive Sleepiness In The Elderly [Causes & Solutions]
How to Monitor Sodium Intake in the Elderly?
Through a collaborative approach considering various factors, families and caregivers can effectively monitor the sodium levels of their loved ones to ensure their overall well-being.
Go Through Food Labels
Teach caregivers or elderly individuals to carefully read the food labels. Analyze the total sodium content per serving. Look for terms like sodium, salt, or sodium chloride that may help in identifying the amount of sodium content in the food.

Consult with a Dietitian
Consider the option of consulting a professional dietitian or nutritionist who may help in generating tailored diet plans for the elderly. A dietitian can assess the dietary intake of an individual and generate a balanced meal plan to meet the needs of each individual according to their health goals and preferences.
Monitor Fluid Intake
Pay close attention to the fluid intake of individuals as it is closely related to sodium imbalance. Promote adequate hydration to avoid any future consequences.
Schedule Regular Checkups
Schedule regular check-ups to keep up with the health condition of the elderly. Arranging regular check-ups can help healthcare professionals assess the sodium levels of the elderly through blood tests and provide an intervention plan considering these checkups.
They can also guide patients regarding their sodium intake after carefully considering their health conditions and medical history.
Keep a Food Diary
One of the most effective and convenient ways to monitor sodium intake in the elderly is to keep a food diary with yourself. Record the foods and beverages consumed and note down the sodium content in each of the drinks and meals consumed. This can effectively help in providing intervention considering the recent sodium intake.
Conclusion
Keeping the sodium levels maintained in the elderly is significant to ensure a healthy life and overall comfort. Through certain strategies, including diet modification, increase in salt content, hydration, and lifestyle changes, sodium levels can be naturally increased in the elderly. Moreover, it is also vital for families and caregivers to pay close attention to the amount of sodium consumed through close observation and modify it accordingly. It is crucial to prioritize the monitoring of sodium intake in our loved ones and offer the care and support that they may require in old age.
FAQs
Does aging affect the body's ability to regulate sodium levels?
Yes, with aging comes multiple other factors such as vulnerability to other diseases and hormonal changes that may play a role in changing sodium levels.
What medications can cause an alteration in sodium levels in our body?
Certain medications such as diuretics, antidepressants, and pain medication may cause an alteration in sodium levels in elder people.
Are there any dietary restrictions related to sodium intake for people with kidney diseases?
Yes, people with kidney disease may have to restrict their sodium intake to manage fluid retention and blood pressure.
Can imbalanced levels of sodium impact independence in the elderly?
Yes, with changes in sodium level comes fatigue, confusion, muscle weakness, and distortion. This can interfere with one's ability to carry out daily life activities effectively, impacting their independence.
What potential risks are associated with sudden changes in levels of sodium in the elderly?
Certain serious complications are associated with altering levels of sodium such as seizures, coma, or cerebral edema in elderly individuals.



![What Are The Pros & Cons of Assisted Living? [2024 UPDATED]](https://caringhandshomecarefl.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Assisted-living-care-pros-cons-e1704122253120-768x612.jpg)
![20+ Signs Your Elderly Is Ready for Assisted Living [2024]](https://caringhandshomecarefl.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Signs-Your-Elderly-Is-Ready-for-Assisted-Living-768x644.jpg)
